
.png)

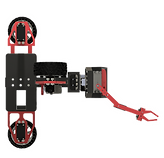
Automated Pipe Traversal
Engineered with a unique staggered X-configuration, PipeX excels at maneuvering through tight bends and corners. Excellent traction is ensured by 4 grip wheels, while servo encoders maintain precise localization,

Traction Control
The active suspension system in PipeX is designed to counteract flow pressures, with the PipeX demo robot able to apply a controlled force of up to 33.2kg on the pipe walls. Combined with the traction wheels, this secures the robot's position, ensuring mobility through steep pipes and flows. This allows the wheelbase to change profiles, giving excellent maneuverability through pipes of various sizes.

Maneuverable Arm
PipeX features a highly maneuverable, pivoting front arm that reaches 360 degrees around the robot. Coupled with computer vision and AI, it scans the pipeline to detect damage and leaks, enabling swift inspection and maintenance.

Camera Vision and AI
The intelligent camera on PipeX’s front arm works hand-in-hand with powerful AI algorithms to scrutinize every detail of the pipe. This smart system identifies damage and pinpoint areas of concern, ensuring that every inspection is both accurate and actionable.
20%
Year-over-year increase in preventable oil and gas extraction fatalities.
$7.6B
Pipeline repair costs for water utilities per year in the U.S alone.
4x
Pipe worker job fatality rates compared to the typical U.S worker job.
PipeX doesn't just save money, it saves lives.

Camera Vision and AI
1
Detecting Points of Interest

Keypoints (in green) are found by changes in intensity of light (left). Clumps of keypoints are marked with the points of interest (right).
2
Determining Features

A mask is applied to the points of interest (left). Contours are created from the mask, and surrounded by boxes to determine the features (right).
AI Classification


